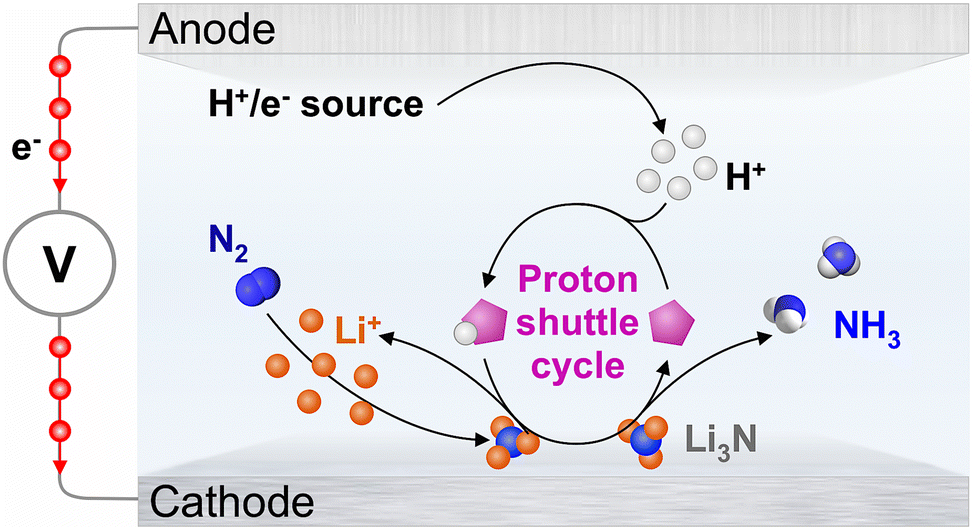
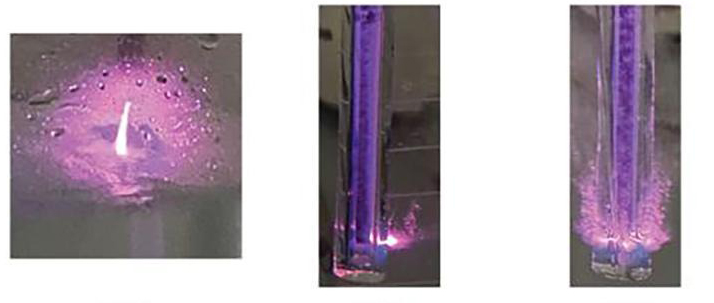
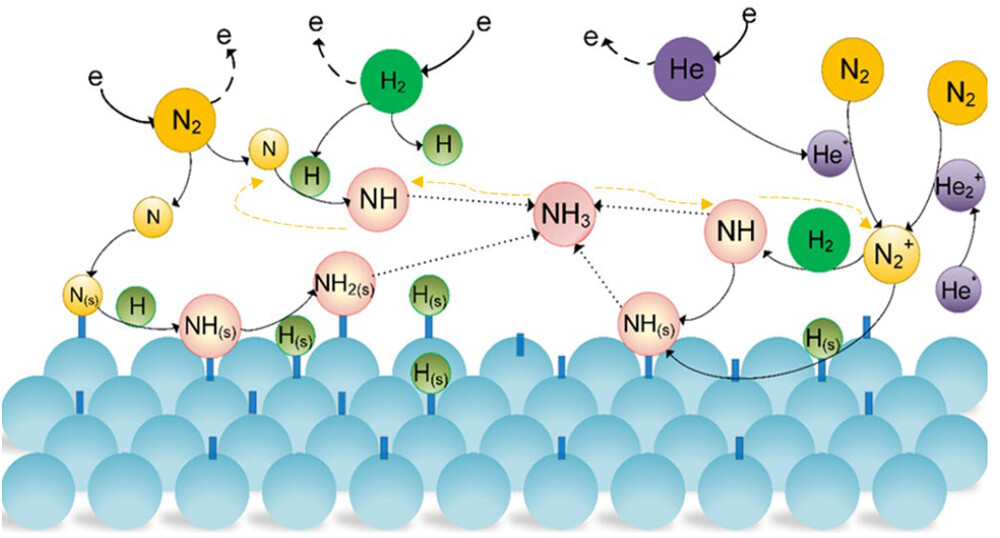
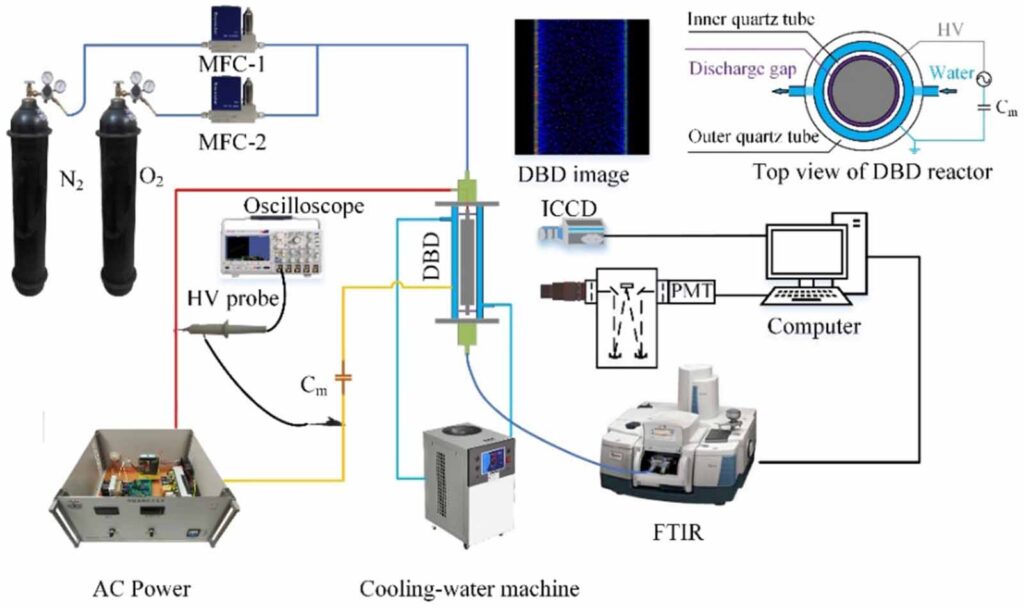
Tackling the interplay between electrocatalysis experiments, theory, characterization, and system complexity
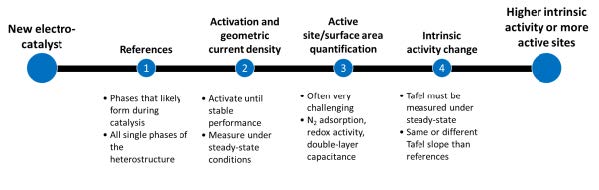
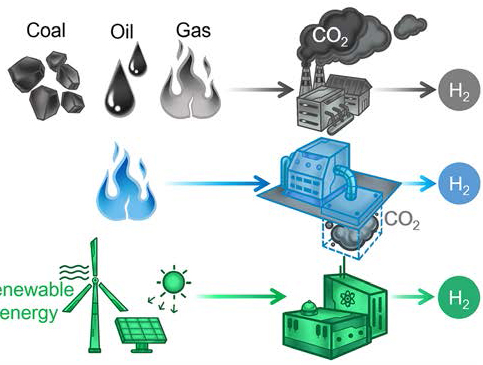
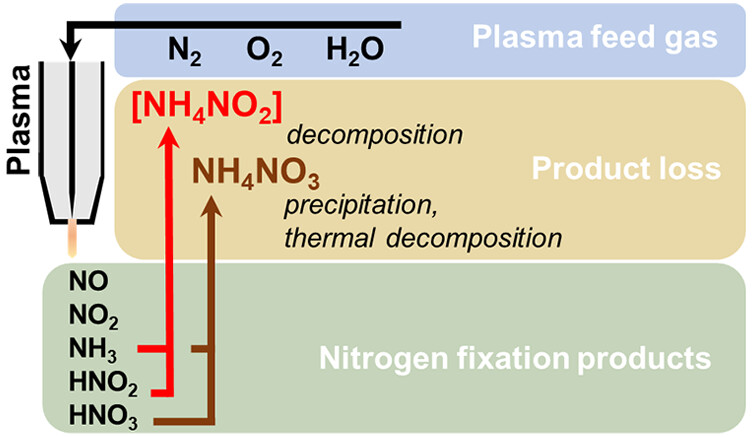
Electrocatalysis is becoming more complex, making it challenging to explore. With so many reports published annually, researchers frequently make electrocatalytic systems more challenging to improve performance. Current electrochemical and analytical methods need help to meet this complexity, making fundamental catalytic aspects elusive. This leads to the development of complex interface-related hypotheses. A pathway with essential […]